Explanation of How Matter Recycles Again and Again by Energy Passes Through an Ecosystem Only Once
1.2: Cycling of Thing
- Page ID
- 33022
INTRODUCTION
The earth's biogeochemical systems involve complex, dynamic processes that depend upon many factors. The three chief factors upon which life on the globe depends are:
- The one-mode flow of solar energy into the earth'south systems. Every bit radiant energy, it is used by plants for food production. Equally rut, it warms the planet and powers the weather system. Somewhen, the energy is lost into space in the form of infrared radiation. Nearly of the energy needed to cycle thing through globe's systems comes from the sun.
- The cycling of matter. Because there are only finite amounts of nutrients available on the world, they must be recycled in club to ensure the continued existence of living organisms.
- The strength of gravity. This allows the earth to maintain the atmosphere encompassing its surface and provides the driving force for the downwards motion of materials in processes involving the cycling of matter.
These factors are disquisitional components to the functioning of the earth's systems, and their functions are necessarily interconnected. The main matter-cycling systems involve important nutrients such as water, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus.
WATER Wheel
The earth is sometimes known as the "h2o planet" because over 70 per centum of its surface is covered by h2o. The physical characteristics of water influence the manner life on earth exists. These characteristics include:
- Water is a liquid at room temperature, and remains as such over a relatively wide temperature range (0-100° C). This range overlaps the annual mean temperature of well-nigh biological environments.
- It takes a relatively large amount of energy to raise the temperature of water (i.e., it has a high heat capacity). For this reason, the vast oceans act as a buffer against sudden changes in the average global temperature.
- Water has a very high heat of vaporization. Water evaporation thus provides a adept ways for an organism to dissipate unwanted heat.
- Water is a good solvent for many compounds and provides a adept medium for chemical reactions. This includes biologically important compounds and reactions.
- Liquid water has a very high surface tension, the force property the liquid surface together. This enables upwards send of water in plants and soil by capillary action.
- Solid water (water ice) has a lower density than liquid water at the surface of the earth. As a issue ice floats on the surface of rivers, lakes, and oceans subsequently it forms, leaving liquid water below where fish and other organisms tin continue to live. If ice were more dense than liquid h2o, it would sink, and bodies of water in cold climates might eventually freeze solid.
All living organisms require water for their continued existence. The water cycle (hydrologic wheel) is composed of the interconnections between water reservoirs in the environment and living organisms and the concrete processes (eastward.g., evaporation and condensation) involved in its transport between those reservoirs. The oceans contain about 97 pct of the total h2o on the planet, which leaves about three percent as fresh water. Nearly of the fresh water is locked up in glacial and cap ice or buried deep in the earth where it is economically unfeasible to extract it. One approximate gives the amount of fresh water available for human utilise to be approximately 0.003 percent of the full amount of fresh water. However, this is really a more than adequate supply, as long as the natural bicycle of water is non severely disturbed by an outside strength such equally man activity.
There are several of import processes that affect the transport of h2o in the water cycle. Evaporation is the process past which liquid water is converted to water vapor. The source of energy for this procedure is normally the dominicus. For example, the lord's day's radiation heats the surface water in a lake causing it to evaporate. The resulting water vapor is thus added to the atmosphere where it tin can exist transported to another location. Ii important effects of the evaporation are cooling and drying.
Transpiration is a process by which water evaporates from living plants. H2o from the soil is absorbed past a constitute's roots and transported to the leaves. There, some is lost as vapor to the temper through modest surface openings.
When water vapor in the atmosphere cools, information technology can transform into tiny droplets of liquid water. This process is chosen condensation, and it can occur every bit water vapor is transported into the cooler upper atmosphere. Dust and pollen in the atmosphere help to initiate the process by providing condensation centers. If the droplets remain pocket-sized enough to be supported by air motions, they tin can group together to class a deject. Condensation can also occur in the air almost the footing as fog or on institute leaves as dew.
When condensed water aerosol grow and then large that the air tin can no longer back up them confronting the pull of gravity, they fall to the globe. This is the process called atmospheric precipitation.
If the water droplets fall as liquid, information technology is called rain. If the temperature of the surrounding air mass is common cold enough to freeze the h2o aerosol, the resultant precipitation tin can be called snow, sleet or hail, depending upon its morphology.
H2o falling on the ground (east.one thousand., every bit precipitation or irrigation), can move downslope over the surface (e.g., surface runoff) or penetrate the surface (east.g., infiltration). The amount of surface runoff and infiltration depends upon several factors: water infall rate, surface moisture, soil or rock texture, type and amount of surface comprehend (e.g., leaves and rooted plants), and surface topography. Surface runoff is the predominate process that occurs subsequently atmospheric precipitation, with nearly of the water flowing into streams and lakes. On a groundslope unprotected past vegetation, runoff tin occur very rapidly and result in severe erosion.
Water that infiltrates the surface can motion slowly downwardly through the layers of soil or porous rock in a process known as percolation. During this process, the water can deliquesce minerals from the rock or soil as it passes through. The water collects in the pores of rocks every bit groundwater when it is stopped by an impermeable layer of rock. The upper limit of this groundwater is known as the h2o tabular array and the region of h2o-logged rock is known equally an aquifer. The groundwater may slowly flow downhill through rock pores until it exits the surface as a spring or seeps into a stream or lake.
Water is the essence of life. In that location would be no life as we know it without h2o. The vast oceans of water exert a powerful influence on the atmospheric condition and climate. Water is besides the agent by which the landforms are constantly reshaped. Therefore, the water wheel plays an important office in the balance of nature.
Man activity can disrupt the natural residue of the water bicycle. The buildup of salts that results from irrigating with groundwater can cause soil infertility and irrigation tin can besides deplete secret aquifers causing land subsidence or salt h2o intrusion from the body of water. The immigration of land for farming, structure, or mining can increase surface runoff and erosion, thereby decreasing infiltration. Increasing human populations and their concentration in certain geographic localities volition keep to stress water systems. Careful thought is needed on local, regional and global scales regarding the utilise and management of water resources for wetlands, agriculture, industry and home.
CARBON Bike
Carbon is the basic building block of all organic materials, and therefore, of living organisms. However, the vast majority of carbon resides as inorganic minerals in crustal rocks. Other reservoirs of carbon include the oceans and temper. Several concrete processes affect carbon as it moves from i reservoir to another. The inter-relationships of carbon and the biosphere, temper, oceans and crustal earth -- and the processes affecting it -- are described by the carbon bike.
The carbon bicycle is actually comprised of several inter-connected cycles. The overall effect is that carbon is constantly recycled in the dynamic processes taking place in the atmosphere, at the surface and in the crust of the earth. For example, the combustion of wood transfers carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide is taken in by plants and converted to nutrients for growth and sustenance. Animals eat the plants for nutrient and exhale carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when they breathe.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean where it eventually precipitates as carbonate in sediments. The sea sediments are sub ducted past the actions of plate tectonics, melted and then returned to the surface during volcanic action. Carbon dioxide gas is released into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions. Some of the carbon atoms in your body today may long agone have resided in a dinosaur'southward trunk, or perhaps were once buried deep in the world's chaff as carbonate rock minerals.
The chief carbon cycling processes involving living organisms are photosynthesis and respiration. These processes are really reciprocal to one some other with regard to the cycling of carbon: photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the temper and respiration returns it. A significant disruption of 1 process can therefore affect the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
During a process called photosynthesis, raw materials are used to manufacture sugar. Photosynthesis occurs in the presence of chlorophyll, a light-green plant pigment that helps the found utilize the energy from sunlight to drive the process. Although the overall process involves a series of reactions, the cyberspace reaction tin can be represented by the following:

The sugar provides a source of energy for other constitute processes and is also used for synthesizing materials necessary for plant growth and maintenance. The net effect with regard to carbon is that information technology is removed from the atmosphere and incorporated into the plant as organic materials.
The reciprocal process of photosynthesis is called respiration. The net result of this process is that sugar is broken down past oxygen into carbon dioxide and water. The net reaction is:
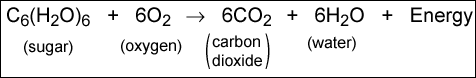
This procedure occurs not just in plants, but also in humans and animals. Unlike photosynthesis, respiration can occur during both the 24-hour interval and nighttime. During respiration, carbon is removed from organic materials and expelled into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Another process by which organic textile is recycled is the decomposition of expressionless plants and animals. During this procedure, leaner interruption down the circuitous organic compounds.
Carbon is released into the soil or h2o as inorganic material or into the atmosphere as gases. Decomposed constitute material is sometimes buried and compressed betwixt layers of sediments. Subsequently millions of years fossil fuels such coal and oil are formed. When fossil fuels are burned, the carbon is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
The carbon cycle is very of import to the beingness of life on earth. The daily maintenance of living organisms depends on the ready availability of different forms of carbon. Fossil fuels provide an of import source of energy for humans, as well equally the raw materials used for manufacturing plastics and other industrially important organic compounds. The component processes of the carbon cycle have provided living things with the necessary sources of carbon for hundreds of millions of years. If not for the recycling processes, carbon might long ago have become completely sequestered in crustal rocks and sediments, and life would no longer exist.
Human being activity threatens to disrupt the natural bike of carbon. Two important ways past which humans take affected the carbon bicycle, particularly in recent history, are: 1) the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during the burning of fossil fuels, and 2) the clearing of trees and other plants (deforestation) that blot carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. The net effect of these actions is to increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. It is estimated that global atmospheric carbon dioxide is increasing by nearly 0.4% annually. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas (i.east., it prevents infrared radiation from the earth'southward surface from escaping into space). The heat is instead captivated past the temper. Many scientists believe that the increased carbon dioxide concentration in the temper is resulting in global warming.
This global warming may in turn cause meaning changes in global weather condition, which could negatively affect all life on earth. Withal, increased photosynthesis (resulting from the increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide) may somewhat counteract the effects. Unfortunately, the issues of fossil fuel burning, deforestation and global warming are intertwined with economic and political considerations. Furthermore, though much studied, the processes are even so not well-understood and their ramifications cannot be predicted with confidence.
NITROGEN Bicycle
The chemical element Nitrogen is of import to living organisms and is used in the production of amino acids, proteins and nucleic acids (Dna, RNA). Molecular nitrogen (N2) is the most arable gas in the atmosphere. Nevertheless, only a few unmarried-cell organisms are able to utilise this nitrogen class straight. These include the bacteria species Rhizobium, which lives on the root nodules of legumes, and cyanobacteria (sometimes called bluish-green algae), which are ubiquitous to water and soil environments. In social club for multi-cellular organisms to use nitrogen, its molecular form (N2) must be converted to other compounds, e.grand., nitrates or ammonia. This process is known equally nitrogen fixation. Microbial organisms such as cyanobacteria deport out nearly of the earth's nitrogen fixation. The industrial manufacture of fertilizers, emissions from combustion engines and nitrogen called-for in lightning business relationship for a smaller fraction.
The nitrogen bike is largely dependent on microbial processes. Bacteria fix nitrogen from the atmosphere in the form of ammonia (NH3) and catechumen the ammonia to nitrate (NO3-).
Ammonia and nitrate are absorbed by plants through their roots. Humans and animals become their nitrogen supplies by eating plants or plant-eating animals. The nitrogen is returned to the cycle when leaner decompose the waste or dead bodies of these higher organisms, and in the process, convert organic nitrogen into ammonia. In a process chosen denitrification, other leaner convert ammonia and nitrate into molecular nitrogen and nitrous oxide (N2O). Molecular nitrogen is thus returned to the atmosphere to beginning the cycle over again.
Humans have disturbed the nitrogen cycle in recent history past activities involving increased fixation of nitrogen. Almost of this increased nitrogen fixation results from the commercial production of fertilizers and the increased burning of fuels (which converts molecular nitrogen to nitric oxide, NO). The use of commercial fertilizers on agricultural lands increases the runoff of nitrates into aquatic environments.
This increased nitrogen runoff stimulates the rapid growth of algae. When the algae die, the h2o becomes depleted in oxygen and other organisms die. This process is known as eutrophication. The excessive use of fertilizers also stimulates the microbial denitrification of nitrate to nitrous oxide. Increased atmospheric levels of nitrous oxide are thought to contribute to global warming. Nitric oxide added to the atmosphere combines with water to form nitric acrid (HNO3), and when nitric acid dissolves in h2o droplets, it forms acid pelting. Acid rain damages healthy trees, destroys aquatic systems and erodes building materials such every bit marble and limestone.
PHOSPHOROUS CYCLE
Phosphorus in world systems is usually in the class of phosphate (PO43-). In living organisms information technology is an essential constituent of cell membranes, nucleic acids and ATP (the carrier of energy for all life forms). Information technology is also a component of bone and teeth in humans and animals. The phosphorus bike is relatively elementary compared to the other cycles of matter as fewer reservoirs and processes are involved. Phosphorus is non a nominal elective of the atmosphere, existing there only in dust particles.
Well-nigh phosphorus occurs in crustal rocks or in body of water sediments. When phosphate-bearing rock is weathered, the phosphate is dissolved and ends up in rivers, lakes and soils. Plants have up phosphate from the soil, while animals ingest phosphorus past eating plants or found-eating animals. Phosphate is returned to the soil via the decomposition of creature waste or constitute and creature materials. This cycle repeats itself again and again. Some phosphorus is washed to the oceans where it somewhen finds its manner into the sea-floor sediments.
The sediments go buried and grade phosphate-bearing sedimentary rocks. When this stone is uplifted, exposed and weathered, the phosphate is once more released for use past living organisms.
The motion of phosphorus from stone to living organisms is normally a very slow process, but some human activities speed up the process. Phosphate-bearing rock is oft mined for employ in the manufacture of fertilizers and detergents. This commercial production greatly accelerates the phosphorous cycle. In improver, runoff from agricultural land and the release of sewage into water systems can cause a local overload of phosphate. The increased availability of phosphate tin crusade overgrowth of algae. This reduces the oxygen level, causing eutrophication and the devastation of other aquatic species. Marine birds play a unique role in the phosphorous cycle. These birds have up phosphorous from ocean fish. Their droppings on land (guano) contain high levels of phosphorous and are sometimes mined for commercial utilise.
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Ecology/AP_Environmental_Science/01:_Chapters/1.02:_Cycling_of_Matter
0 Response to "Explanation of How Matter Recycles Again and Again by Energy Passes Through an Ecosystem Only Once"
Post a Comment